If you have kidney damage and/or a decrease in kidney function for three or more months, it is called chronic kidney disease (CKD).
There are five stages of CKD, with progressive symptoms.
-
Stage 1
Includes signs of mild kidney disease, with a normal GFR showing 90 percent or higher kidney function.
-
Stage 2
Includes signs of mild kidney disease with a GFR showing 60–89 percent kidney function.
-
Stage 3
Includes signs of moderate kidney disease and a GFR showing 30–59 percent kidney function.
-
Stage 4
Includes signs of severe kidney disease and GFR showing 15–29 percent kidney function.
-
Stage 5
Includes signs of severe kidney disease and kidney failure, with a GFR showing less than 15 percent kidney function.
-
These indicators can occur in all stages
- May have some blood in urine
- May have urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- May have kidney stones
- Can have aneurysms in brain
-
Treatment options to discuss with your doctor
- Limit protein intake
- Limit salt intake
- Consider hypertension medication
-
PKD Stages 1–2
- Few physical symptoms
- Labs may show slightly elevated creatinine
-
PKD Stages 3–4
May have no physical symptoms or may have:
- Fatigue
- Back pain
- Puffiness or swelling
- Loss of appetite
- Food may taste funny
- Hypertension
- Abdominal swelling
-
PKD Stage 5
Physical symptoms include:
- Anemia
- Weak, tired, drowsy
- Headaches
- Confusion, difficulty concentrating
- Nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite
- Itching
- Muscle cramps
- Swelling and puffiness
- Shortness of breath
- Hypertension
- Change in skin color (grayish or yellowish)
- Women may experience changes in menstrual cycle
It is important to keep your doctor informed of your symptoms so she/he can help you decide when it’s time to start dialysis or be evaluated for transplant.
Symptoms that some people experience during this time could include:
- Decreased energy
- Weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Weight loss
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Mild to moderate depression
- Decreased ability to think problems through
Blood tests will show that your blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine are not being properly eliminated by the kidneys and are building up in the blood. These tests may also show that your electrolytes and pH are out of balance.
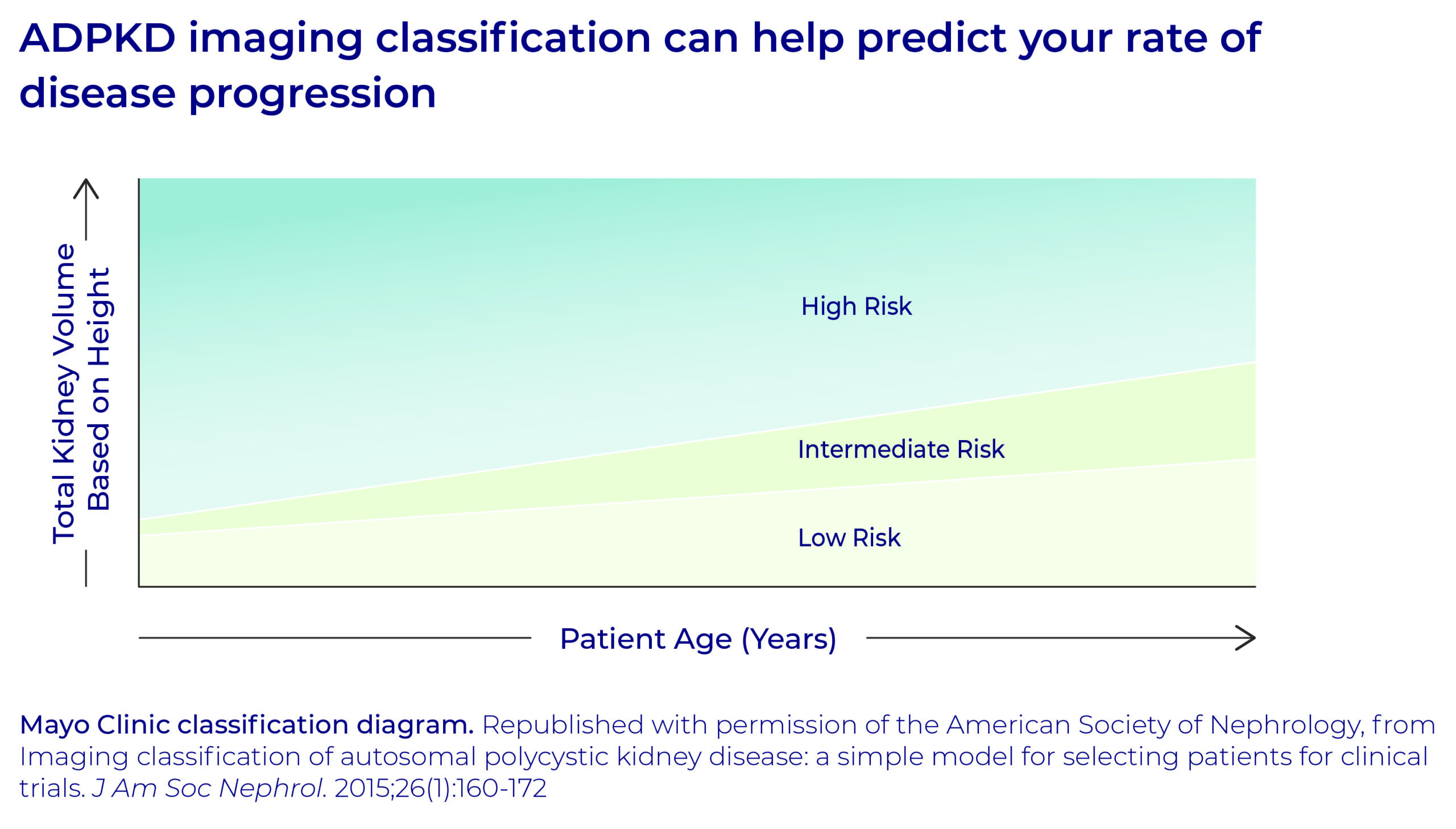
Generally, planning for kidney replacement therapy (dialysis) is done when your kidney function is at about 25 percent. If you wait until you are very sick, it will take you much longer to recover and may require hospitalizations.